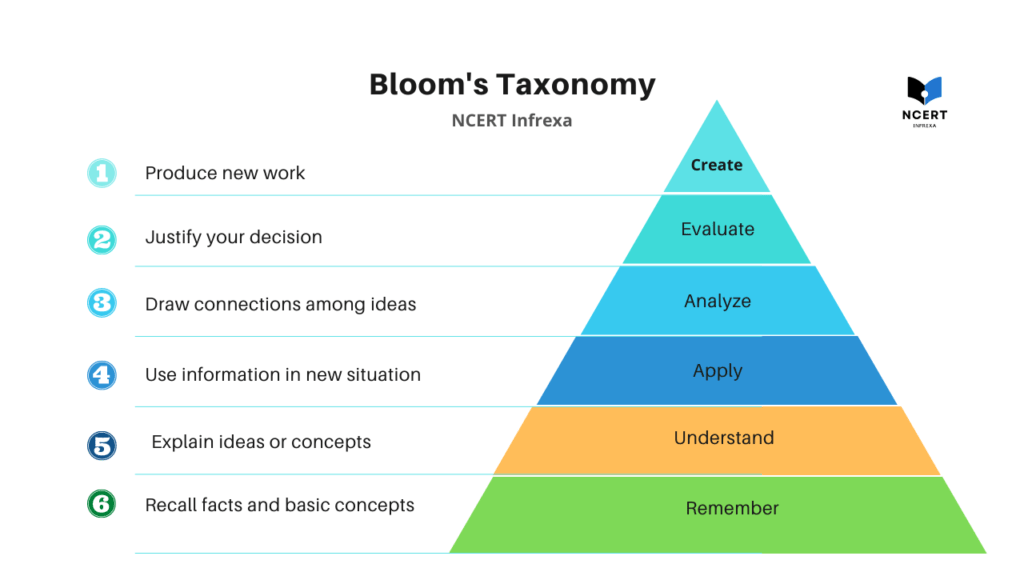
Bloom’s Taxonomy, also known as the “Taxonomy of Educational Objectives,” is an educational framework authored by Benjamin Bloom and his four collaborators – Max Englehart, Edward Furst, Walter Hill, and David Krathwohl in 1956.
Key Highlights of Bloom’s Taxonomy
- Revised for the 21st Century: While originally published in 1956, the taxonomy was revised in 2001 (The Revised Taxonomy 2001) to reflect modern needs and learning styles. Key updates include using action verbs instead of nouns and prioritizing the different “knowledge types” used in cognition.
- Six Levels of Learning: Bloom’s Taxonomy outlines six cognitive levels: Remembering, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating, and Creating. Each level builds upon the previous one, demanding increasingly complex thinking skills.
The Original Taxonomy (1956)
Published in 1956, Bloom’s Taxonomy aimed to provide a framework applicable to generations of K-12 teachers and college instructors in their teaching methods.
| Document | Bloom’s Taxonomy |
| Author (s) | Benjamin Bloom, Max Englehart, Edward Furst, Walter Hill, and David Krathwohl |
| Year | 1956 |
| Place | University of Chicago |
| Revision | The Revised Taxonomy – 2001 |
This version consisted of six (categories) cognitive domains:
- Knowledge: Recalling facts, terms, and basic concepts.
- Comprehension: Understanding the meaning of information.
- Application: Applying knowledge to new situations.
- Analysis: Breaking down information into its component parts.
- Synthesis: Incorporates the creative, mental construction of ideas and concepts from multiple sources to form new, integrated, and meaningful patterns..
- Evaluation: Making judgments based on observations or informed rationalizations.
Each category includes its subcategories, all lying along a continuum from simple to complex and concrete to abstract. The last five categories are presented as “skills and abilities,” with the understanding that knowledge is a necessary precondition for applying these skills and abilities.
Related: Learn 5 types of Communication Skills with these great examples
For a comprehensive understanding, you can download a PDF of Bloom’s Taxonomy, which defines all terms mentioned above with well-structured examples.
The Revised Taxonomy (2001)
The revised taxonomy employs 25 verbs to aid in understanding students’ behavior and learning outcomes. It replaces nouns with verbs and gerunds to achieve educational objectives dynamically.
The following are some of the key action words:
- Remembering
- Understanding
- Applying
- Analyzing
- Evaluating
- Creating
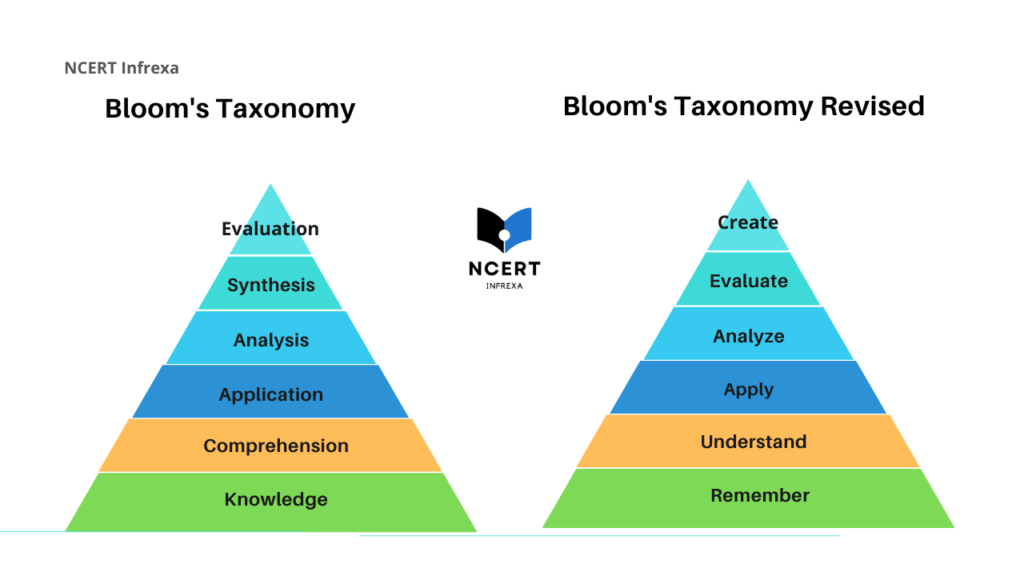
In the revised taxonomy, knowledge remains central to the six cognitive processes. However, it is further categorized into types of knowledge used in cognition:
- Factual Knowledge
- Conceptual Knowledge
- Procedural Knowledge
- Metacognitive Knowledge
For a detailed comparison between Bloom’s Taxonomy and its revised version, refer to the provided PDF.
Goals, Aims, and Objectives of Bloom’s Taxonomy
Bloom’s Taxonomy aims to provide a multi-tiered scale for expressing the level of expertise required to achieve measurable student outcomes. It organizes measurable student outcomes, enabling teachers to select appropriate assessment techniques for their courses. The main objectives include:
- Knowledge-based goals
- Skills-based goals
- Affective goals (values, attitudes, and interests)
Each goal has its taxonomy, detailed in the attached PDF, with levels of expertise organized in increasing complexity.
Importance
Bloom’s Taxonomy serves as a map for facilitating education. Just as Chacha Nehru, an Indian thinker, emphasized the importance of child education, Bloom’s Taxonomy aims to develop students’ capabilities effectively.
Providing a roadmap for teachers ensures quality learning and shapes the academic future of students and nations.
Applications in Education
Educators can use it to:
- Craft clear and measurable learning objectives.
- Design diverse assessment methods that go beyond simple recall.
- Promote higher-order thinking skills like critical analysis and problem-solving.
- Cater to various learning styles and individual needs.
Conclusion
Bloom’s Taxonomy provides a convenient way to describe the degree to which students understand and use concepts, demonstrate skills, and have their values affected. Determining the expected levels of student expertise helps in selecting appropriate assessment techniques. Additionally, it fosters critical thinking and higher-order cognitive abilities, ultimately promoting students’ ability to create.