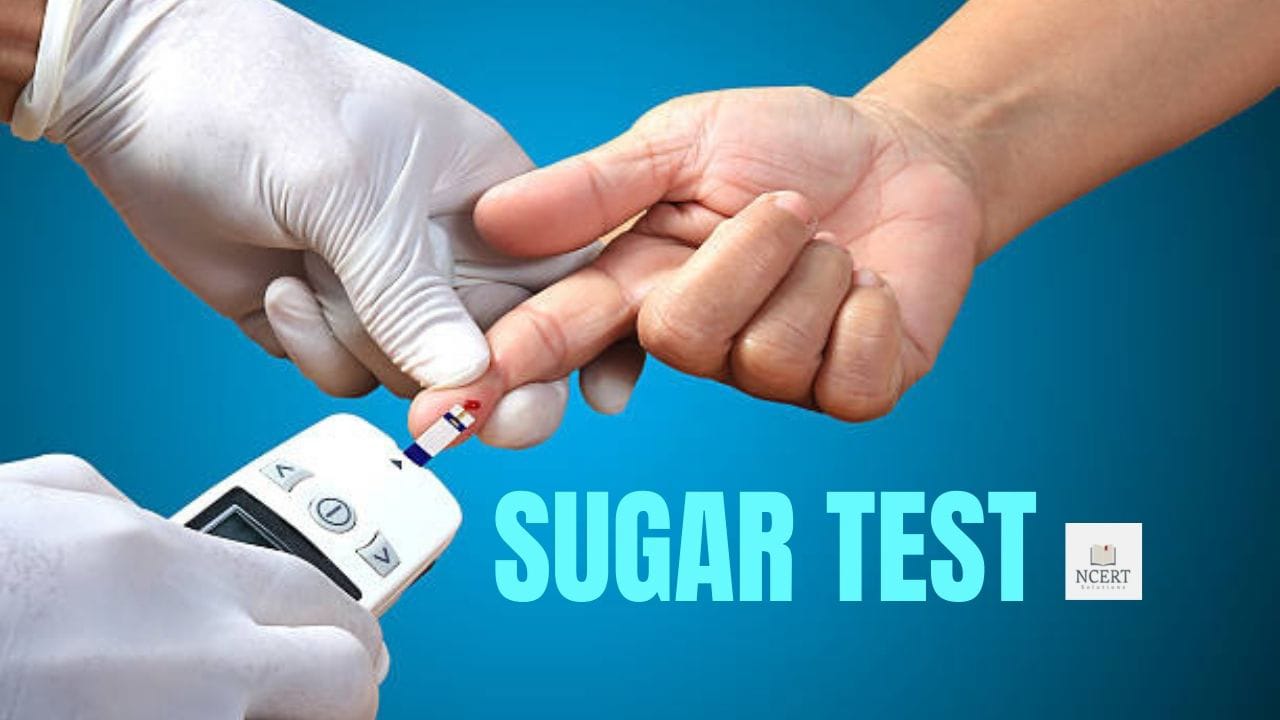
A blood sugar or glucose test measures the amount of sugar (glucose) in the blood, glucose is a type of sugar, which is present in the blood.
Glucose is the main source of energy for the cells of the body, these cells also include brain cells.
Glucose is a type of normal sugar, which is the main source of energy for the body. Your body converts the carbohydrates you consume into glucose.
When carbohydrates start rapidly converting into glucose in the body, the level of sugar or glucose in the blood starts increasing.
What is Blood Sugar (Glucose) Test
Blood sugar (glucose) test gives immediate results. This test gives you the information you need to decide on the following things –
- Is your blood sugar level high or low?
- Does your diet or exercise need to change?
- Are your diabetes medicines or treatments working?
- Is your treatment going as expected or not?
Even if you don’t have diabetes, your doctor may ask you to include this test in your routine checkup. Or, it may be done to see if you are at risk of developing diabetes.
If any of the following factors are true for you, you have an increased risk of developing diabetes:
- If you are 45 years of age or more.
- If you are overweight.
- If you don’t exercise.
- If you have high blood pressure, triglycerides or cholesterol levels.
- If you have a history of insulin resistance.
- If you have a family history of diabetes.
You can test blood sugar in two ways:
- People who have diabetes can use a glucometer on a daily basis to keep track of it.
- If someone just wants to get the test done once or twice a year, then they can go to the lab and get the test done.
Your doctor may order two types of blood sugar tests:
- ‘Fasting blood sugar test’, which measures your current blood sugar level.
- ‘Hemoglobin A1c test, which shows your blood sugar level for the last 90 days.
The results of these tests will tell whether you have prediabetes or diabetes.
Why it is done
Your doctor may order a blood sugar test to see if you have pre-diabetes or diabetes. This test measures the amount of glucose in your blood.
Your body takes carbohydrates from foods like grains and fruits and turns them into glucose. Glucose (a type of sugar) is one of the main sources of energy for your body.
There are tests available for diabetics to monitor their blood sugar levels that can be done at home.
The results of this test will reveal your own blood sugar level, so you can see if you need to make changes to your diet, exercise, or diabetes medicines.
What happens when blood sugar levels are too high or too low:
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) can cause seizures, or you can go into a coma. This happens only in rare cases.
- High blood sugar (hyperglycemia) can lead to ‘ketoacidosis’. This is a very dangerous condition for you, which is often a concern for people with type 1 diabetes. Ketoacidosis occurs when your body starts using fat only for fuel.
Before the Blood Sugar (Glucose) Test
The blood sugar (glucose) test can be done either as a random test (under normal conditions) or as a fasting test (without eating anything).
In the fasting test, 8 hours before the test, doctors advise avoiding drinking and eating anything except water. The doctor may also recommend doing the blood glucose fasting test in the morning, as doing so will prevent you from being hungry for the whole day.
Before the random sugar or glucose test, you can eat the normal things you eat every day.
Doctors mostly recommend fasting tests, because their results are more accurate and their results are easier to interpret.
If you are taking any kind of medicines, supplements or other herbal products, etc., then tell the doctors about it before the test.
Some types of medicines can affect blood sugar levels. If you take certain types of medicines, your doctor may ask you to stop those medicines for a while or make some changes in the dosage before the test.
Medicines that affect blood sugar levels may include:
- Acetaminophen
- Steroids
- Diuretics
- Birth control pills
- Hormone therapy
- Aspirin
- Antipsychotics
- Antidepressants
- Phenytoin
- Sulfonylurea drugs
Chronic stress can also increase the level of glucose or sugar in the blood, which can usually be due to the following factors:
- Surgery
- Trauma
- Stroke
- Heart Attack
If you have had any of these problems before, then definitely tell the doctor about it.
During Blood Glucose (Sugar) Test
It is similar to a normal blood test, in which a sample of blood is taken from a vein for testing. Before removing the sample, the place where the needle is to be inserted is cleaned with an antiseptic and all the germs are killed.
After that, an elastic band or bandage is tied on the upper part of the arm, due to which the flow of blood in the veins stops and the veins start to swell.
When the veins become clearly visible due to swelling, then a needle is inserted into one of them. The blood drawn from the vein is pumped into a vial or tube attached to the needle.
After Blood Sugar (Glucose) Test
After the test, slight pain or discomfort may be felt from where the sample was taken and there may also be a blue mark there. Which may disappear automatically after some time.
When the needle goes inside the skin, some people feel a little pain at that time, after removing the needle, the place is pressed a little so that the scar is not left.
After removing the sample, it is sent to the laboratory for testing. After the result comes, the doctor starts the treatment after discussing it with you.
What are the risks of this Test?
There are no or very few risks and side effects in a blood sugar test. You may have pain or swelling where the needle was inserted, especially if the sample is taken from your vein.
Blood Sugar (Glucose) Test Normal Range and Result
1. General Result
Fasting: If you’ve had a fasting blood sugar (glucose) test, a level between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter is considered the normal range.
Non-fasting: If you have a random blood sugar (glucose) test, the normal result depends on the last time you ate. Most of the time, the blood glucose level remains less than 125 milligrams per deciliter.
2. Abnormal Result
Fasting blood sugar or glucose test is done:
- A level between 100 and 125 milligrams per deciliter may indicate that your glucose level is impaired while on an empty stomach, a type of pre-diabetes.
- A level of 125 mg per deciliter or above usually indicates diabetes.
If a random blood (non-fasting) sugar or glucose test is done:
- A level of 200 milligrams per deciliter or above in you usually indicates diabetes.
- Depending on your random blood sugar or glucose test results, your doctor may recommend a fasting blood sugar (glucose) test or HbA1C test.
- If a person has been tested for diabetes, abnormal random blood results may mean that the diabetes is not being controlled properly.
Table to understand the result values
| Results | Fasting | Non-fasting |
|---|---|---|
| Normal range | 70-100 | Less than 125 |
| Abnormal range | 100 -125 (Pre-diabetic) Above 125 (diabetic) | above 200 |
3. HbA1c Test (HbA1c)
In a person without diabetes, it usually occurs in up to 5.7 percent. For a diabetic patient, it is 7.0 percent or less.
Certain other medical problems can also cause blood sugar or glucose levels to be higher than normal, such as:
- An overactive thyroid gland.
- Pancreatic cancer
- Pancreatitis (swelling, burning, redness, etc.) of the pancreas
- Stress due to trauma, stroke, surgery or heart attack
Low blood sugar or glucose levels (hypoglycemia) can be caused by:
- Hypopituitarism (a disorder of the pituitary gland)
- Underactive thyroid gland or adrenal gland
- Tumors in the pancreas
- Excessive use of insulin or other diabetic drugs Liver disease
- Kidney Diseases
- Weight Loss After Surgery
- Exercising vigorously
When to get tested with Blood Sugar (Glucose) Test
If you are showing signs of diabetes, your doctor may suggest a blood glucose test. Doctors mostly suggest getting a fasting blood glucose test done.
This test can also be used to monitor the level of diabetes in people who already have diabetes.
A blood sugar (glucose) test may also be done in the following situations:
- Frequent urination,
- If your weight is gaining suddenly
- Blurred vision
- Hallucinations, changes in normal behavior and way of talking,
- Fainting
- Epilepsy (for the first time) etc.
If you are overweight (BMI level of 25 or higher) and have any of the following risk factors, you should talk to your doctor about getting tested.
- If your previous blood sugar test level was high.
- Blood pressure 140/90 mm Hg or higher or unhealthy cholesterol level.
- Have had heart diseases in the past.
- Women who have been tested for diabetes during pregnancy.
- Polycystic ovary disease is a condition in women in which the balance of female sex hormones is disturbed, causing cysts in the ovaries.
- If someone in your close relationship has diabetes (eg parent, brother or sister, etc.)
- If you are not physically active.