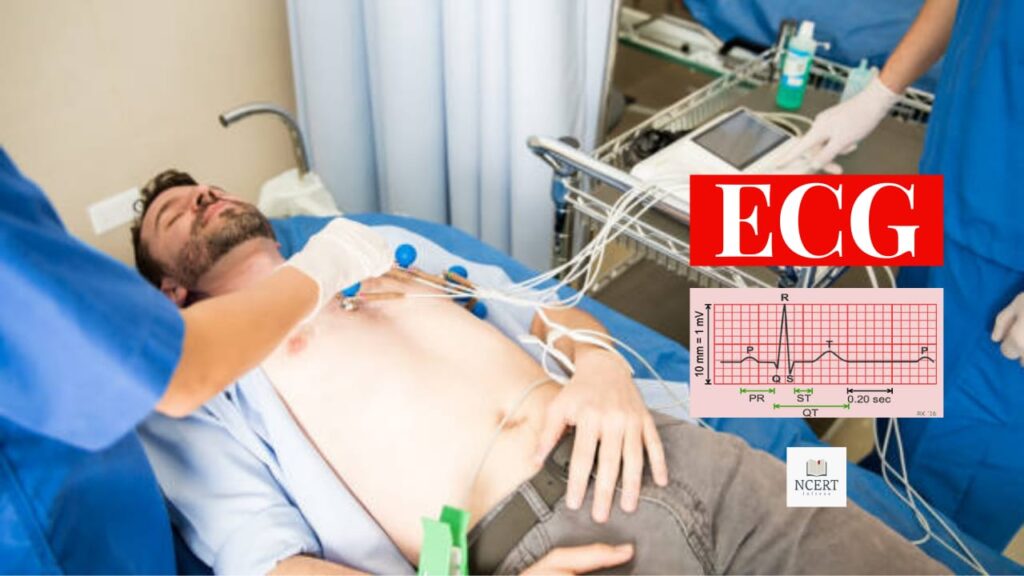
An Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a simple, painless test that records the electrical activity of your heart. Each heartbeat is triggered by an electrical signal, and the ECG captures these signals to assess how well your heart is functioning.
Purpose of an ECG
Doctors use ECGs to:
- Check for irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias).
- Detect heart attacks or evidence of past heart attacks.
- Assess the size and position of the heart chambers.
- Monitor the effectiveness of heart disease treatments.
- Evaluate symptoms like chest pain, dizziness, or shortness of breath.
Types of ECG Tests
- Resting ECG: Performed while you’re lying down, it records the heart’s activity at rest.
- Stress Test (Exercise ECG): Conducted while you exercise on a treadmill or stationary bike to see how your heart performs under stress.
- Holter Monitor: A portable device worn for 24-48 hours to record continuous heart activity during daily activities.
- Event Monitor: Similar to a Holter monitor but used over longer periods. You activate it when you feel symptoms.
Preparing for an ECG
- Avoid applying lotions or oils on your skin before the test, as they can interfere with electrode placement.
- Wear comfortable clothing; you may need to remove your shirt for electrode placement.
- Inform your doctor about any medications you’re taking.
During the ECG
- You’ll lie down, and a technician will place electrodes on your chest, arms, and legs.
- These electrodes are connected to the ECG machine, which records your heart’s electrical signals.
- The test typically takes a few minutes.
Understanding ECG Results
Normal Results:
- Heart rate between 60-100 beats per minute.
- Consistent and regular heart rhythm.
- No signs of damage or abnormalities.
Abnormal Results May Indicate:
- Irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias).
- Heart attacks (current or past).
- Enlarged heart chambers.
- Electrolyte imbalances.
- Poor blood supply to the heart.
Note: According to the National Library of Medicine, some abnormal results can be due to factors like body position, movement during the test, or even electrode placement. Always discuss results with your doctor.
Risks of an ECG
An ECG is safe and non-invasive. The only minor risk is slight skin irritation where electrodes are placed.
Real-Life Example
Imagine a 50-year-old man experiencing occasional chest discomfort. His doctor recommends an ECG, which reveals an irregular heartbeat. Further tests confirm atrial fibrillation, and treatment begins promptly, reducing his risk of stroke.
Read also: छाती में गैस के लक्षण: हार्ट अटैक या गैस का दर्द कैसे पहचानें?
Conclusion
An ECG is a valuable tool for detecting heart problems early. It’s quick, safe, and provides essential information about your heart’s health. If you experience symptoms like chest pain or dizziness, consult your doctor about the need for an ECG.