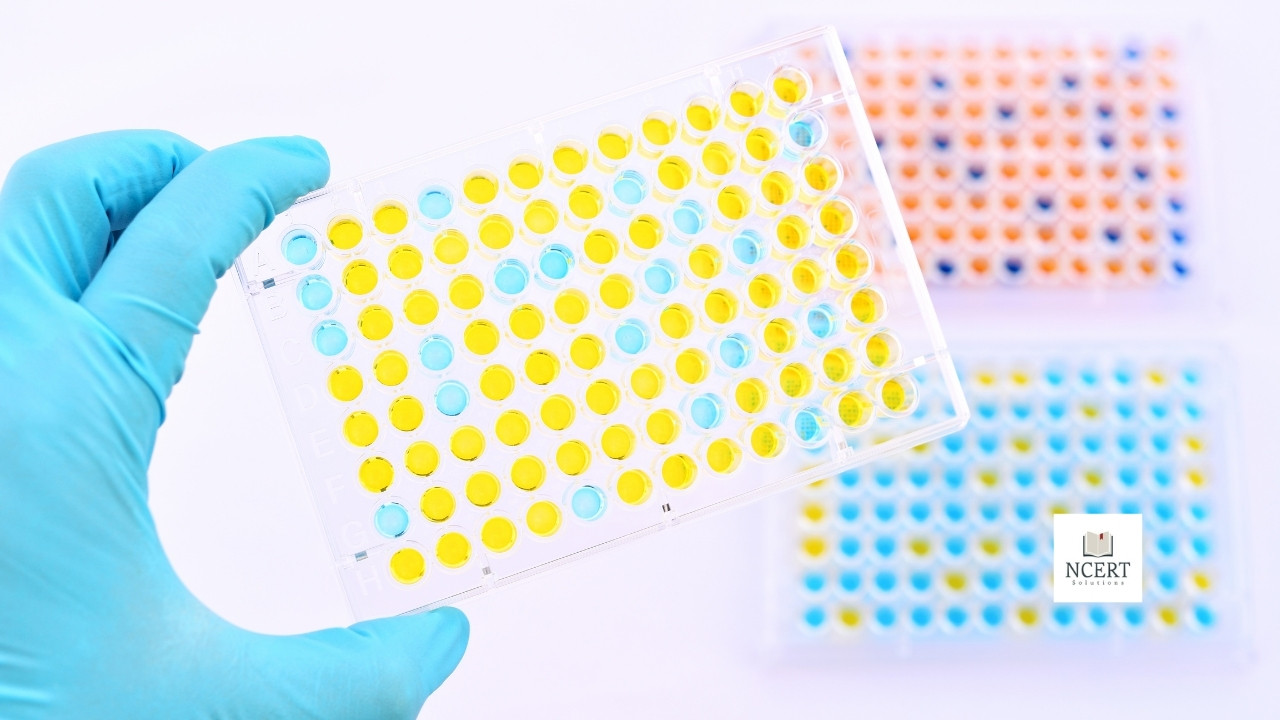
The ELISA test is used to find out how the body’s immune system is reacting to microbes. Through this test, chemicals and other elements present in the immune system are checked. The ELISA test contains an enzyme (a protein that enhances a biochemical reaction).
Antibodies or antigens in the body are checked with the help of an ELISA test. Antibodies are made by the body’s immune system to fight a disease or infection. An antigen is a foreign substance that stimulates the immune system (such as stimulating it to produce antibodies) against infections or diseases.
Further in this article, you are being told about the ELISA test. You will learn when, why, and how the ELISA test is performed, as well as how much it costs. You will also know how to prepare before this test and what are precautions to be taken after the test.
What is the ELISA test? Full form of ALISA test
As many people often search across the internet for the full form of the ELISA test, here we are letting you know about it. ELISA stands for “enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay“.
Its main goal is to show the presence of antibodies or antigens in a blood sample, which is formed when a disease or infection develops in the body.
| Full form | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| First described by | Engvall and Perlmann |
| Year | 1971 |
| Detects | Presence of antigen or antibody |
| Used for | Detection of – HIV, SARS-CoV-2, Dengue, and Hepatitis etc |
As the full form of the ELISA test suggests – “enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay”, the ELISA test is mainly used to detect a protein that is antagonistic to molecules and ions, like glucose and potassium. Hormones, viral antigens (Such as Dengue fever), bacterial antigens (such as TB), and antibodies can be detected by ELISA tests.
Why is the ELISA test done?
The ELISA test, sometimes referred to as the “EIA test”, detects the presence of antibodies and antigens in the blood. If you have an infection, an ELISA test can be used to find out whether your body is making antibodies against it. Antibodies are a type of protein that the immune system makes to react against harmful substances (antigens).
The doctor may ask for an ELISA test to test for the following diseases and other conditions:
- HIV (The virus that causes AIDS)
- Lyme disease
- Pernicious anemia
- Rotavirus
- Nipah virus
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Syphilis
- Zika virus
- Toxoplasmosis
- Varicella-zoster virus causes chickenpox and shingles.
Doctors can often use this test to monitor the condition while performing a complex test. If you are experiencing symptoms and signs associated with the above conditions, then the doctor may suggest you get an ELISA test done.
Apart from this, if the doctor wants to find out any of the above problems then they can use the ELISA test.
What is done before the ELISA test?
No special preparation is required before doing this test. A needle is inserted into the vein to remove a sample of blood for the test, which causes a slight pain or prickling feeling for a few seconds.
If you think that taking the sample may make you feel faint or dizzy, tell your doctor before the test.
How is the ELISA test done?
For the test, a sample of your blood is taken, which is usually taken from a vein in the arm. First of all, the doctor cleans the skin with antiseptic at the place from where the blood has to be removed. After that, the doctor puts a bandage on the upper part of the arm, due to which the flow of blood in the veins stops and the veins start swelling.
They become visible when the veins swell and the doctor inserts a needle into a vein. A syringe or vial is attached to the needle in which the blood is collected.
What is done after this test?

When a sufficient amount of sample is removed for the test, the doctor removes the needle and places a small piece of cotton wool or a bandage on the area.
The doctor may also ask you to apply light pressure on the area for some time after removing the needle, which prevents bleeding and scarring. This test procedure is much more painless than many other tests, but after the test, you may feel a short tingling or slight discomfort in your arm.
After removing the sample, it is sent to the laboratory for testing. In the laboratory, a blood sample is put in a glass plate, which contains certain types of antigens. If there are antibodies in the blood, they bind with the antigen. The testing technician then adds a specific type of enzyme to it and checks how your blood and antigens react to this particular type of enzyme.
What are the risks of the ELISA test?
One person’s veins and arteries may be different in size and structure from another person’s. Even the veins and arteries of one part of a person’s body may differ in size and shape from another part of their own body. Therefore, it may be more difficult to draw a blood sample from a person’s veins than from other people.
The risks associated with taking a blood sample are minor and can include:
- Excessive bleeding
- Feeling faint or spinning
- Hematoma (Blood clotting under the skin)
- Infection (There may be some slight risk of infection from a needle piercing in the skin)
What do these test results mean?
There can be hundreds of types of ELISA tests, so the result and meaning of this test also depend on the type of test itself.
A single ELISA test result is not considered negative or positive. Because the ELISA test is very sensitive and in some people, its result appears positive even if it is negative.
Lupus, Lyme disease, and other sexually transmitted infections can also cause an ELISA test to sometimes give a positive result for HIV/AIDS. Therefore, if the result of the ELISA test comes back positive, it needs to be confirmed with another test.
However, if both the ELISA and the second confirmatory test detect the virus, then the virus is likely to be present.
If the results of both tests are negative – if you have been exposed to the HIV virus within the last 3 months, then it is present in your body but not found in the test result. In such cases, the person should get tested again within the next three months. During this time, they should take precautions to prevent the spread of the virus.
If one of the tests is positive, then you need to seek the help of a doctor immediately. The doctor may also suggest other types of tests to confirm the results. Special treatment arrangements can also be designed if needed.
ELISA tests for HIV
It is important to mention that doctors often recommend ELISA tests for HIV. If your doctor suspects anything wrong he asks you to have this test done first.
ELISA Test is the first test to detect the infection caused by HIV. The test is repeated or other tests are done to get 100% confirmation of the disease.
SEE THIS ALSO :
- PCV Test कई परीक्षणों में से एक है जिसका उपयोग एनीमिया (खून की कमी से होने वाली एक बीमारी) की जाँच के लिए किया जाता है
- A urine test is one of the effective Health screening procedures.
- डायबिटीज/मधुमेह के मरीज भूलकर भी न करें ये काम, जानलेवा हो सकता है।
- डॉक्टर आपके साथ बदसलूकी करे तो यहाँ शिकायत कर उसका लायसेंस रद्द करवा दें।
- सावधान! यात्रा करने से पहले वाहन में देख ले स्टीकर वर्ना हो सकता है बड़ा हादसा।